This feature is part of VTEX Shield. If you're already a VTEX client and would like to adopt VTEX Shield for your business, contact our Commercial Support. Additional fees may apply. If you're not a VTEX client yet but are interested in this solution, please complete our contact form.
In system integrations, especially when exchanging sensitive information or controlling business operations, it's essential to ensure that both ends of the communication are secure. mTLS is a feature of VTEX Shield that adds an advanced layer of security to integrations between external systems and VTEX.
Key concepts
Before understanding how mTLS works in practice, let's review two fundamental concepts in system integration: client-server architecture and digital certificates.
Client-server architecture
All API-based communication between systems follows a client-server architecture. In this model, one system (the client) sends a request, and the other (the server) returns a response. In traditional TLS/HTTPS communication, only the server presents a digital certificate, which the client then verifies.
Digital certificates
A digital certificate works like an electronic ID that a system uses to prove its identity during a connection. These certificates are issued by a Certificate Authority (CA), which acts as a trusted third party to validate digital identities.
- The server presents its certificate, and the client checks if it was issued by a trusted CA.
- With mTLS, the process is bidirectional: in addition to the server presenting a certificate, the client also presents its own certificate, and the server checks if it was issued by the right CA.
This mutual certificate exchange allows both sides to verify each other's identity, significantly increasing the security of the integration.
How mTLS works
Unlike standard TLS, which encrypts traffic based on server authentication only, mTLS requires both the client and the server to present valid digital certificates.
With mTLS, only trusted systems can communicate with each other. This reinforces the security of integrations and prevents unauthorized access. In other words, all communication between a headless storefront and VTEX or between an ERP and VTEX, in either direction, is protected by mutual authentication and encryption, ensuring that no unauthorized connections can access or manipulate the data being exchanged.
The diagram below represents the mutual authentication flow using mTLS, where client and server validate each other's identity before any data is exchanged:
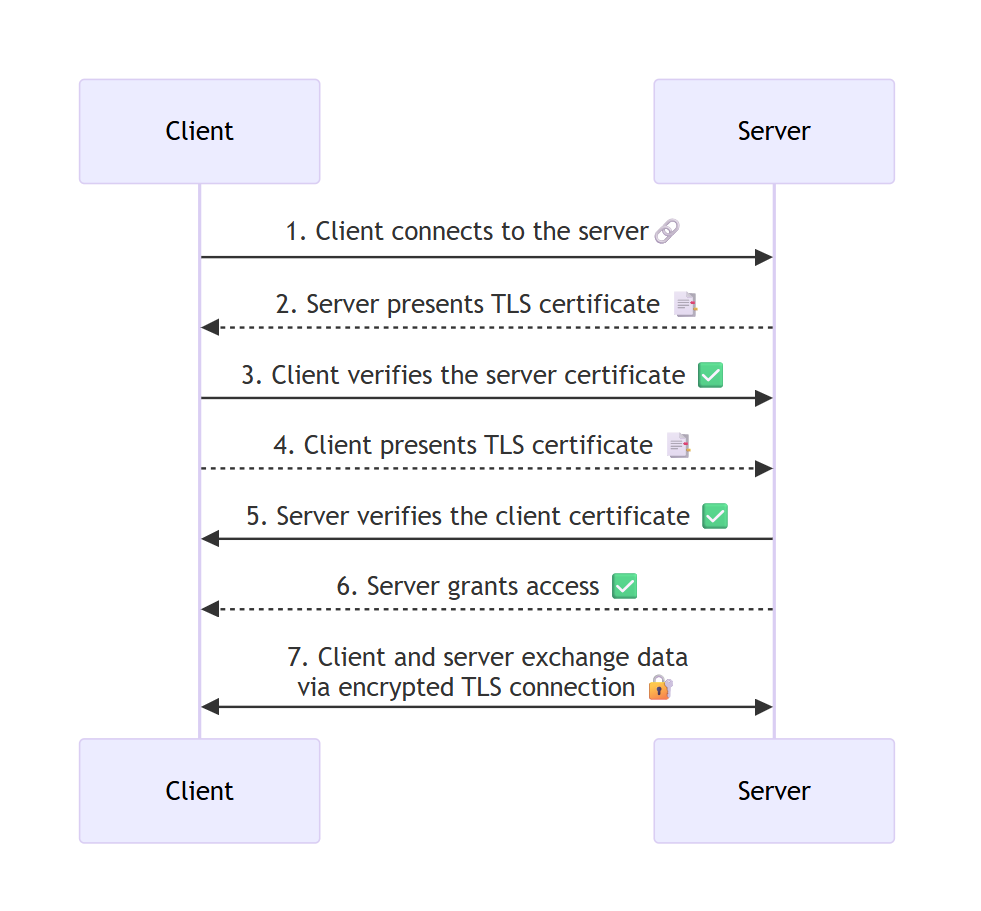
- The client initiates a connection to the server.
- The server presents its TLS certificate.
- The client verifies if the server's certificate is valid.
- The client presents its own TLS certificate.
- The server checks the client's certificate.
- After mutual verification, access is granted.
- Communication proceeds securely, encrypted, and based on trust between both sides.
mTLS flow on VTEX
Here's how the flow applies to communication between VTEX and merchant systems. Depending on the case, VTEX may act as either the client or the server.
| Request direction | Description |
|---|---|
| Headless store or ERP/WMS → VTEX | When a request is sent from the store to VTEX, it's routed to an incoming mTLS proxy located within our VPC. The proxy validates the certificate in the request, checking if it was issued by the CA of VTEX. The request is forwarded to internal microservices only after successful validation. |
| VTEX → Headless store or ERP/WMS | If VTEX sends a request to the store, the traffic goes through an outgoing mTLS proxy in our VPC, which injects a certificate issued by the CA of the merchant. This allows the merchant's environment to check the authenticity of the request and accept only legitimate, secure connections. |
Advantages
These are the main benefits of using mTLS on VTEX:
-
Mutual authentication: Client and server validate each other's identity before any data is exchanged, preventing unverified access attempts.
-
End-to-end encryption: All data is encrypted, protecting sensitive customer information and transaction details from interception.
-
Seamless integration: Merchants can easily integrate mTLS with their commerce APIs and third-party applications, reducing complexity and risk.
-
Flexible protection: you can choose to enable mTLS on specific integrations — such as payment providers or ERPs — allowing you to tailor the security level to your specific use cases.
Protection against attacks
By authenticating both sides of the connection, mTLS helps protect against the following types of attacks:
-
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM): Also known as "on-path" attacks, this occurs when malicious agents position themselves between the client and server to intercept or alter communications. With mTLS enabled, attackers can't authenticate themselves as a client or server, making this type of attack virtually impossible.
-
Malicious API calls: mTLS ensures that only legitimate, authenticated users can make API calls. This prevents attackers from sending malicious requests aimed at exploiting vulnerabilities or manipulating API behavior.
-
Spoofing attacks: Attackers can try to "spoof" a web server to deceive a user (or the other way around). Because mTLS requires valid TLS certificates on both sides, spoofing attacks become significantly more difficult.
-
Credential stuffing: Cybercriminals use leaked credential combinations to gain unauthorized access. Credential stuffing attacks are ineffective against organizations that use mTLS, as attackers can't authenticate without a valid TLS certificate.
Requirements
Since mTLS is a protection for integrations between systems, the system on the other end of the connection with VTEX must also be a system, such as middleware that processes the frontend of a headless integration or calls to an ERP or WMS.
Therefore, to use mTLS, the store must meet at least one of the following requirements:
-
Operate in a headless model, where all interactions with VTEX are performed through API-based integrations.
The use of mTLS doesn't apply to implementations with a native storefront, such as Store Framework or Portal CMS Legado.
-
Have one or more API-based integrations with external services (ERP, WMS, external sellers, etc.).
Additional requirements for integrations involving VTEX responses
In any scenario where VTEX needs to send requests back to the merchant's environment — such as integrations with external sellers or login flows — the following requirements apply:
- The merchant must have their own CA. This CA issues the certificate that VTEX will present, allowing the merchant to validate the authenticity of incoming requests from VTEX.
- The merchant's server must be configured to request or require the client's certificate during the TLS handshake. This is usually done by adjusting the SSL/TLS settings to enable mutual authentication, ensuring that both sides of the connection can validate their identities before any data is exchanged.
Usage modes
mTLS can be implemented across all systems or in specific integrations, offering flexibility based on the security needs of the store. Learn more about the available modes below.
mTLS across all systems
- Provides comprehensive mTLS protection for all incoming and outgoing communication between VTEX and the merchant's destination servers.
- Ensures that every data exchange is protected by mutual authentication, which secures all API interactions across the entire ecosystem.
mTLS for specific integrations
- Provides mTLS protection only in specific integrations instead of covering all endpoints.
- Protects selected connections to external services, such as ERP and WMS/TMS systems, external sellers, and other third-party systems.